Review: (all Review Points taken from Page 17)
1) Energy of electrons increases as you move away from the nucleus.
2) You cannot pinpoint the exact location of an electron - only the general area (Heisenburg Uncertainty Principle - loosely)
3) Bohr put electrons in orbitals.
Waves:
Frequency is inversly proportional to wavelength
- As frequency increases, wavelength decreases (gets shorter)
- As frequency decreases, wavelength increases (gets longer)
The formula for the relationship between frequency and wavelength is:
Why do I care about waves?
1) Light travels in waves
2) Electrons are made of light
Light
- Travels in waves
- Very fast
- Electromagnetic Spectrum
How does this apply to Chemistry?
- Electrons are photons of light
- Atoms have an emission spectrum!
* called the Atomic Emission Spectrum
* Seen when an excited atom passes through a gas
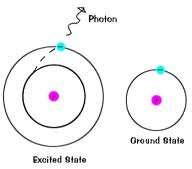
How does it work?
1) Atom absorbs a certain amount of energy
3) Moves back down to its normal energy level (Ground State)
- emits a packet of energy (quanta or photon) as it does this
4) We can see this emission of energy
- comes out as color!
- Metals heat up and change color
- Max Planck wanted to explain this change of color
* determined that energy changes in set units (quanta)
- Planck's Constant
* Pertains to amount of energy released when an excited electron goes back to its Ground State
* States: The amount of radiant energy (E) absorbed or emitted is proportional to the frequency of the
radiation absorbed.
Planck's Constant = 6.6262 x 10 ^-34 Js
Websites:
Click Here for an explanation of quanta, or photon.
Click Here for an explanation of Planck's Constant.
Click Here for the history and explanation of Planck's Constant.














 You can find multiple things on this Periodic Table (PT from here on out).
You can find multiple things on this Periodic Table (PT from here on out).